Garage Openers - PFC CONTROLS | Miami, Gate Operators, Sliding Gate, Swing Gate, Intercoms, Turnstiles, Bollards, Barrier gate
- GATE ACCESS
- PEDESTRIAN ACCESS
- CONTACT US
- Main Menu
- GATE ACCESS
- PEDESTRIAN ACCESS
- CONTACT US
2026 Top Die Casting Molds What to Know Before You Buy?
As industries evolve, understanding the intricacies of Die Casting Molds becomes paramount. In a recent report from Market Research Future, it’s projected that the die casting market will reach $91.66 billion by 2026. This growth reflects the increasing demand for lightweight and durable components in sectors like automotive and aerospace. According to industry expert Dr. Jane Holloway, "Choosing the right die casting mold can make or break your manufacturing efficiency."
Navigating the purchase of Die Casting Molds requires careful consideration. Factors such as material choice, mold design, and production volume significantly influence their effectiveness. The importance of these molds in ensuring product quality cannot be overstated. Yet, many buyers overlook critical aspects, leading to costly mistakes.
Investors need to remain vigilant. A misplaced focus on initial costs can detract from long-term value. Understanding the specific requirements of your production can mitigate potential challenges. Reflecting on these details is not just beneficial; it’s necessary for success in a competitive market.
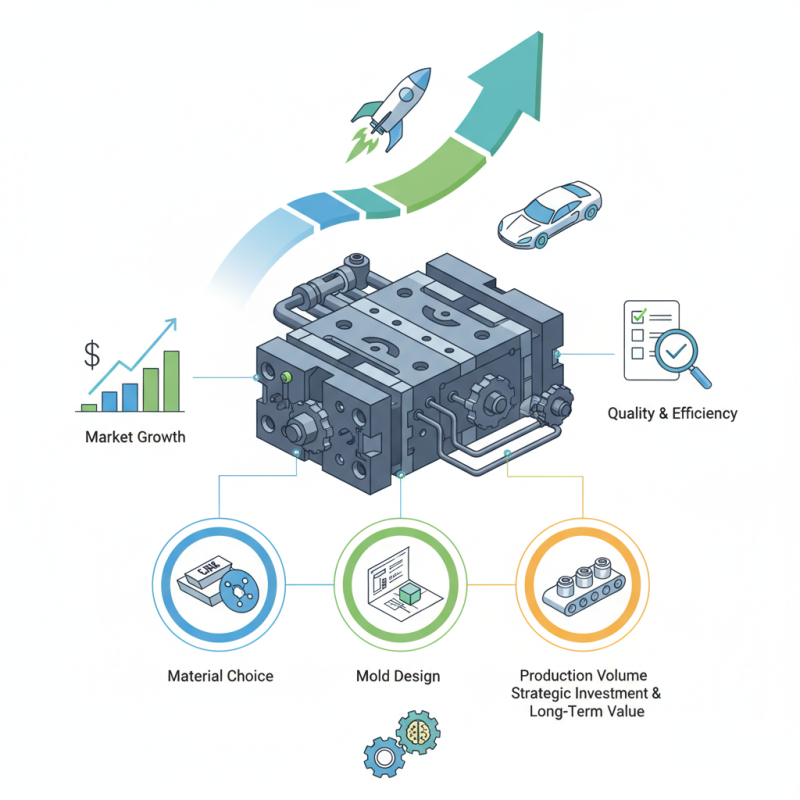
Factors to Consider When Choosing Die Casting Molds
When selecting die casting molds, several factors play a crucial role in your decision. The material of the mold is essential. Aluminum and steel are common choices. Aluminum molds are lightweight and heat conductive. They offer lower costs but may wear out faster. Steel molds are durable and can withstand high pressures, but they are heavier and more expensive.
Another important aspect is mold design. Complex geometries may require advanced techniques. Detailed CAD modeling can help assess manufacturability. A survey by the Die Casting Industry Association indicates that 35% of mold failures stem from poor design choices. It's vital to collaborate with experts to ensure your design is feasible.
Consider the intended production volume as well. For high-volume production, investing in high-quality molds pays off in the long run. However, for lower quantities, cost-effective options may be more sensible. Industry data suggest that about 40% of companies choose molds without adequately considering their production needs. This oversight can lead to significant losses. Reflecting on these factors can help you make better choices.
Material Selection for Die Casting Molds: Key Options Explored
When selecting materials for die casting molds, several key options come into play. Aluminum alloys are popular due to their lightweight and excellent thermal conductivity. They cool quickly, which speeds up production. However, they might wear faster compared to other materials. This wear can lead to increased maintenance costs over time.
Steel, particularly tool steel, is another common choice. It is extremely durable and can withstand high pressures. However, steel molds are heavier and can require longer lead times to produce. The thickness of the steel can also influence heat distribution, affecting the final product's quality. Undoubtedly, a balance must be struck between durability and manufacturing efficiency.
Another option is copper alloys, known for their superior thermal conductivity. They lead to shorter cycle times but can be costly. The trade-off is worth considering, especially for high-volume runs. Ultimately, the decision should reflect your specific production needs and budget constraints. Explore these choices carefully; each comes with its advantages and challenges.
Understanding the Design Process for Effective Die Casting Molds
Designing effective die casting molds requires careful planning and attention to detail. The initial phase involves understanding the intended application. What kind of part are you producing? Consider the material properties. Will aluminum or zinc be more suitable for your needs? These decisions impact every aspect of the mold’s design.
Next, create a detailed mold design. It helps to collaborate with experienced professionals. They can provide insights into potential challenges. Often, the balance between complexity and functionality is tricky. Precise measurements are crucial; even small errors can lead to costly defects. Think about the cooling system. Proper cooling speeds up cycle times and improves the product’s quality.
Finally, consider the manufacturing process. Misalignment during production can compromise the mold’s integrity. Conduct tests to refine your design. It’s essential to analyze the test results and make iterative improvements. This stage is about learning from mistakes. Reflect on what worked and what didn’t. Continuous refinement leads to better outcomes in die casting mold production.
2026 Top Die Casting Molds - What to Know Before You Buy?
| Feature | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Common materials include aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. | Choose based on strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. |
| Mold Design | Design includes drafts, cores, and parting lines. | Ensure ease of ejection and maintain mold integrity. |
| Cooling Systems | Advanced cooling can improve cycle times and part quality. | Assess the layout for optimal thermal management. |
| Surface Finish | Options include matte, polished, or textured finishes. | Select based on aesthetic and functional requirements. |
| Cost Factors | Factors include material, size, and complexity of the mold. | Budget accordingly to avoid overspending. |
| Lead Time | Time required to design and manufacture molds. | Plan for potential delays in production or materials. |
Cost Analysis: Budgeting for Your Die Casting Molds Purchase
When budgeting for die casting molds, start by understanding the costs involved. The price can vary widely. Factors include material type, complexity, and production volume. Molds made from high-quality steel last longer but cost more. On the other hand, aluminum molds may be cheaper but wear out faster.
Don’t forget to account for maintenance and repair costs. Over time, molds can degrade and need professional attention. This can lead to unexpected expenses. Additionally, consider the cost of mold design. Collaborating with expert designers can increase upfront expenses but often results in more efficient production.
Evaluate your project's demands carefully. Analyze the potential return on investment. It’s important to ensure that your budget aligns with your production goals. Take time to reassess your options. A poorly planned purchase can lead to regrettable finances later. Balancing quality and cost is essential for long-term success.
Maintenance and Longevity of Die Casting Molds: What to Expect
When considering die casting molds, maintenance is crucial for longevity. Proper care can extend the life of your molds significantly. Typically, a well-maintained mold can last for several years. Regular inspections are essential. Look for signs of wear and tear. Small issues can become big problems if not addressed promptly.
Tip: Keep the molds clean. Regular cleaning prevents buildup that could affect production quality. Consider using non-abrasive cleaning agents to avoid damaging the surface.
Temperature fluctuations can also impact mold lifespan. Always monitor the temperatures during the casting process. High temperatures can warp molds over time. Ensure that cooling systems are functioning correctly to maintain optimal temperatures.
Tip: Schedule routine maintenance checks. This proactive approach often reveals hidden problems. Investing time in upkeep can save costs in the long run. Keep track of maintenance records to identify patterns in wear. You may notice areas needing extra attention.
Some molds may need replacement sooner than expected. It's important to plan for this possibility. Analyze your production volume and adjust maintenance schedules accordingly. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions in the future.
